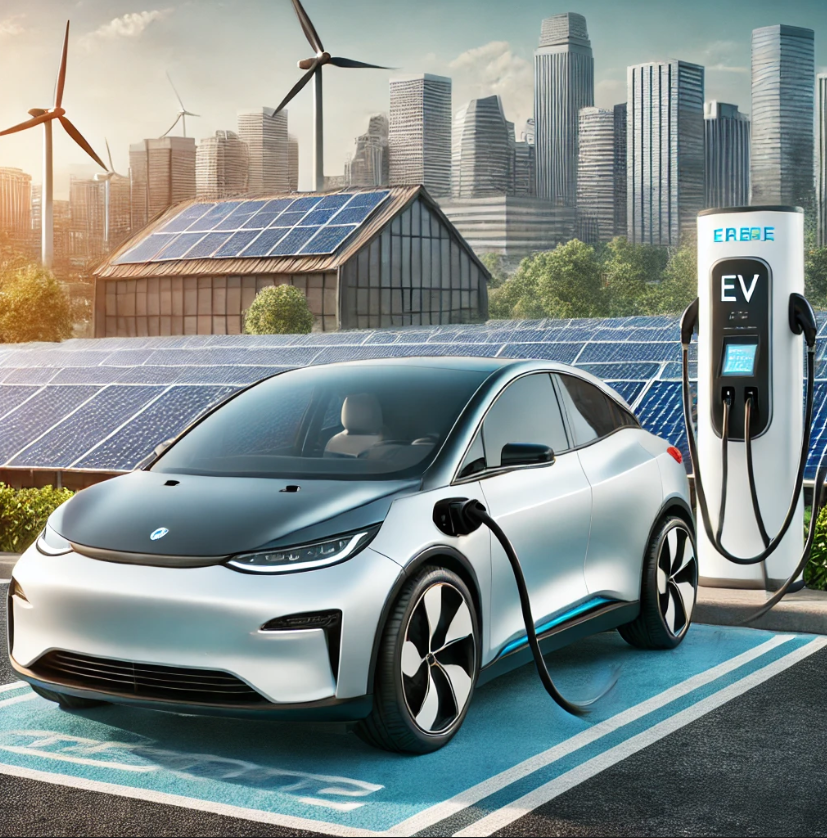
In recent years, electric vehicles (EVs) have transcended niche status, evolving into a vital part of the automotive industry’s future. With leading manufacturers investing in research and development, the shift toward sustainability is driven by factors such as consumer demand for greener technologies, advances in battery efficiency, and supportive legislation from governments worldwide.
Market Growth and Popularity
The EV market has seen unprecedented growth, fueled by increased environmental awareness and advancements in electric technology. Global sales figures for EVs have skyrocketed, indicating their acceptance as a mainstream alternative. Companies like Tesla, Nissan, and new entrants such as Rivian and Lucid Motors have expanded consumer choice and competition. This competition has spurred developments in battery range and design, making EVs more practical for everyday use.
Battery Technology and Range Improvements
One of the initial barriers to widespread EV adoption was limited battery capacity. Early models often struggled to provide more than 100-150 miles per charge, which created “range anxiety” among potential buyers. However, breakthroughs in lithium-ion technology and solid-state batteries have improved ranges, with modern vehicles now achieving up to 400 miles on a single charge. Innovations like regenerative braking also extend the efficiency of these batteries, contributing to a more sustainable and user-friendly driving experience.
Infrastructure Developments
Charging infrastructure has also evolved rapidly. Public and private investments have led to a significant increase in fast-charging stations across urban and rural areas. Companies like Electrify America and Tesla’s Supercharger network have set standards for quick and reliable charging. Additionally, governments are supporting EV adoption through subsidies, tax incentives, and grants aimed at reducing the upfront cost of purchasing electric cars and improving infrastructure.
The Role of Sustainable Manufacturing
Beyond the cars themselves, manufacturers are focusing on sustainability in their production processes. Companies have started integrating recycled materials into their vehicle designs and implementing energy-efficient practices within their factories. The use of renewable energy to power production plants further aligns with the goal of reducing carbon footprints.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite the promising advances, challenges remain. The raw materials for batteries, such as lithium and cobalt, are associated with environmental and ethical issues, including high energy extraction costs and labor rights concerns. The industry is responding by researching alternative battery chemistries, such as lithium-iron-phosphate and exploring recycling programs to reclaim valuable materials.
The future holds potential for not only enhanced vehicle range and performance but also for an increase in renewable integration, such as solar charging solutions and energy storage that uses vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology. The ongoing development of hydrogen fuel cells as a supplement to battery technology could also widen the range of sustainable options available.