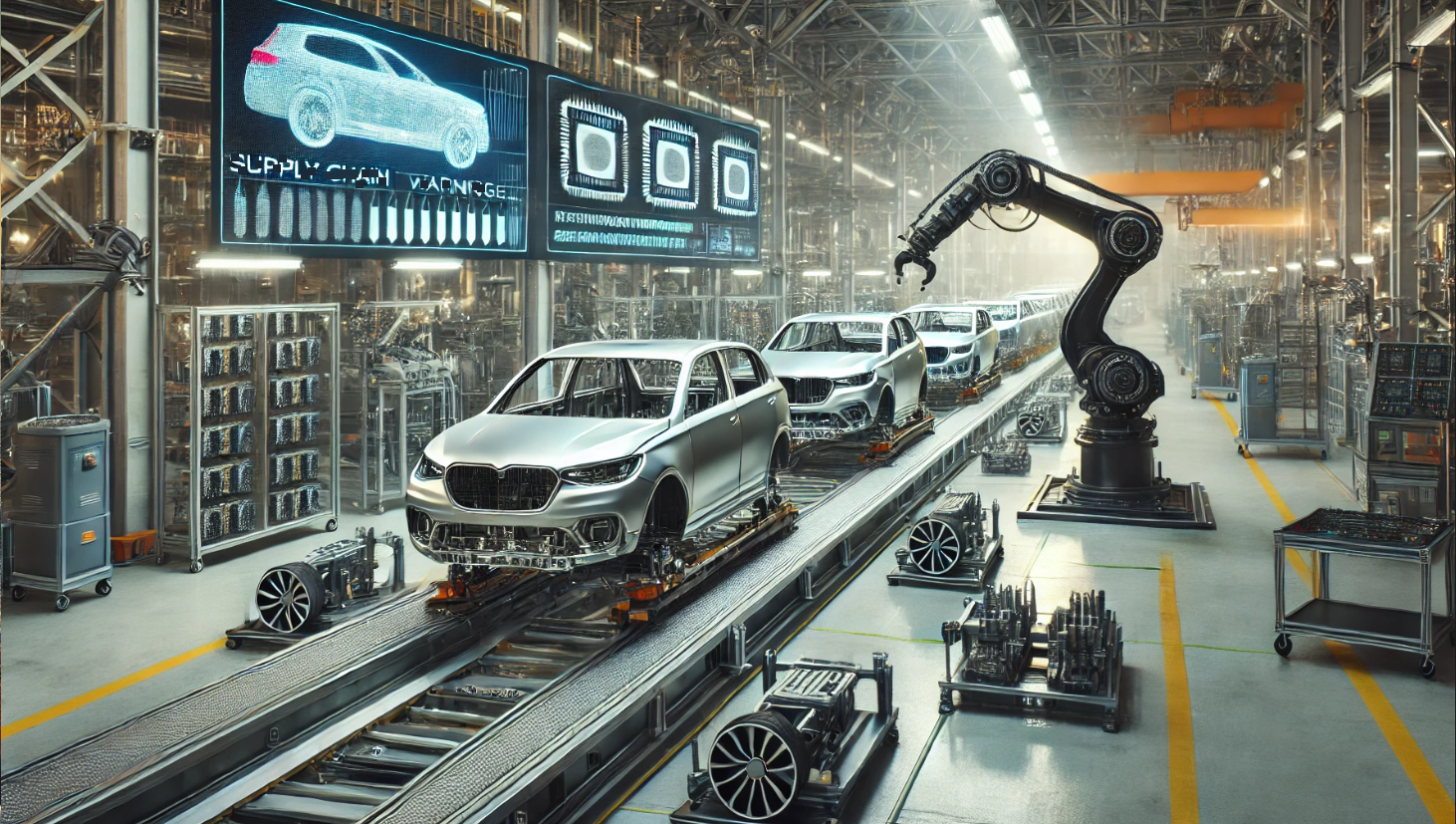
In recent years, the global automotive industry has faced an unprecedented crisis. Car production delays, supply chain disruptions, and rising costs have created a challenging environment for automakers and consumers alike. Several factors contribute to this situation, including the shortage of microchips, difficulties in sourcing essential components, and geopolitical tensions affecting global trade. This article explores the key reasons behind the slowdown in car production and how automakers are adapting to these challenges.
The Microchip Shortage: A Critical Issue for Automakers
One of the most significant reasons for the slowdown in vehicle production is the shortage of semiconductor microchips. Modern vehicles rely heavily on these chips, which control everything from infotainment systems to advanced driver-assistance features. The demand for microchips skyrocketed during the COVID-19 pandemic as consumers purchased more electronics, creating a supply chain bottleneck that affected multiple industries, including automotive manufacturing.
How Did the Chip Shortage Happen?
The microchip shortage was triggered by several factors:
- Increased Demand for Consumer Electronics
- During lockdowns, consumers purchased more laptops, smartphones, and gaming consoles, leading to a surge in semiconductor orders from electronics companies.
- Automakers, on the other hand, reduced their chip orders in anticipation of lower vehicle sales. However, when demand for cars rebounded faster than expected, manufacturers found themselves at the back of the queue for semiconductor supplies.
- Factory Closures and Natural Disasters
- Major chip manufacturing facilities in Asia were temporarily shut down due to COVID-19 outbreaks, causing supply chain disruptions.
- In 2021, a fire at the Renesas semiconductor plant in Japan and extreme weather conditions in Texas, where key semiconductor factories are located, further exacerbated the shortage.
- Geopolitical Tensions Between the U.S. and China
- The ongoing trade war between the United States and China has complicated semiconductor production and distribution.
- The U.S. imposed restrictions on China’s largest chipmaker, Semiconductor Manufacturing International Corporation (SMIC), which limited its ability to produce and export chips to automakers globally.
The Impact on Car Production
The semiconductor shortage has forced automakers to scale back production, delay new model launches, and even remove certain tech features from vehicles. Companies like Ford, General Motors, and Volkswagen have had to shut down assembly lines due to a lack of necessary components. Some brands have opted to sell cars with fewer features, such as the removal of touchscreens or advanced driver-assistance systems, in order to maintain production levels.
Shortages of Other Critical Components
While microchips have received the most attention, they are not the only components in short supply. The automotive industry relies on a vast and complex network of suppliers, many of whom are facing their own challenges.
Supply Chain Disruptions
- Raw Material Shortages
- The prices of essential materials like steel, aluminum, and lithium have surged due to high demand and supply chain constraints.
- Lithium, a key component in electric vehicle (EV) batteries, has seen record price increases, impacting EV production.
- Transportation Bottlenecks
- Global shipping delays and port congestion have slowed down the delivery of essential parts.
- Shortages of truck drivers and logistical workers have further disrupted supply chains, causing longer lead times for vehicle production.
- Labor Shortages in Manufacturing
- The COVID-19 pandemic led to a decline in the workforce as many workers either left the industry or were forced to stay home due to restrictions.
- Skilled labor shortages have made it difficult for factories to operate at full capacity.
The Impact on Prices and Availability
Due to these shortages, the cost of producing vehicles has risen significantly. Many automakers have passed these costs onto consumers, leading to higher car prices across both new and used vehicle markets. Some models that were once readily available now have months-long waiting lists, frustrating potential buyers.
Geopolitical Factors and Their Influence on the Automotive Market
Geopolitical tensions and economic policies have also played a significant role in the crisis affecting the automotive industry.
The Russia-Ukraine Conflict
The war in Ukraine has had direct and indirect effects on car production:
- Ukraine is a major supplier of neon gas, which is essential for semiconductor manufacturing. The conflict has disrupted this supply, worsening the chip shortage.
- Many Western automakers, including Volkswagen and Mercedes-Benz, have shut down their factories in Russia, losing a key market and source of revenue.
- Sanctions on Russian oil and gas have driven up energy prices, increasing production and transportation costs for automakers.
U.S.-China Trade Relations
The strained relationship between the U.S. and China continues to impact the global automotive supply chain:
- Tariffs on Chinese-made auto parts and batteries have led to increased costs for manufacturers that rely on Chinese suppliers.
- China, a dominant force in the production of EV batteries, has restricted exports of key raw materials such as rare earth metals, creating further supply chain vulnerabilities.
How Automakers Are Adapting to the Crisis
Despite these challenges, car manufacturers are implementing various strategies to mitigate the effects of supply chain disruptions and production slowdowns.
1. Diversifying Supply Chains
- Automakers are shifting away from reliance on a single region for critical components. For example, companies are investing in chip manufacturing facilities in the U.S. and Europe to reduce dependency on Asian suppliers.
- Tesla and other EV manufacturers are securing direct partnerships with lithium mining companies to ensure a stable battery supply.
2. Adjusting Production Strategies
- Some manufacturers are prioritizing high-margin vehicles (such as SUVs and luxury cars) over lower-margin models to maximize profitability during the crisis.
- Others have resorted to producing vehicles with missing features, allowing customers to install certain components later when supplies become available.
3. Investing in Domestic Manufacturing
- Governments worldwide are incentivizing local production of semiconductors and EV batteries to strengthen supply chains.
- The U.S. CHIPS and Science Act, for instance, provides funding to increase domestic semiconductor production and reduce reliance on foreign sources.
4. Emphasizing Software-Defined Vehicles
- Some automakers, like General Motors and Volkswagen, are shifting towards software-based vehicle architectures that allow for remote updates and the ability to activate features post-purchase once components become available.
Conclusion
The automotive industry is experiencing one of its most significant crises in recent history, driven by semiconductor shortages, supply chain disruptions, and geopolitical conflicts. While car manufacturers are taking steps to address these challenges, the road to full recovery remains uncertain. As the industry adapts through diversification, local production, and new business models, consumers will need to navigate longer wait times and higher prices in the near future. However, these changes may ultimately lead to a more resilient and technologically advanced automotive industry in the years to come.