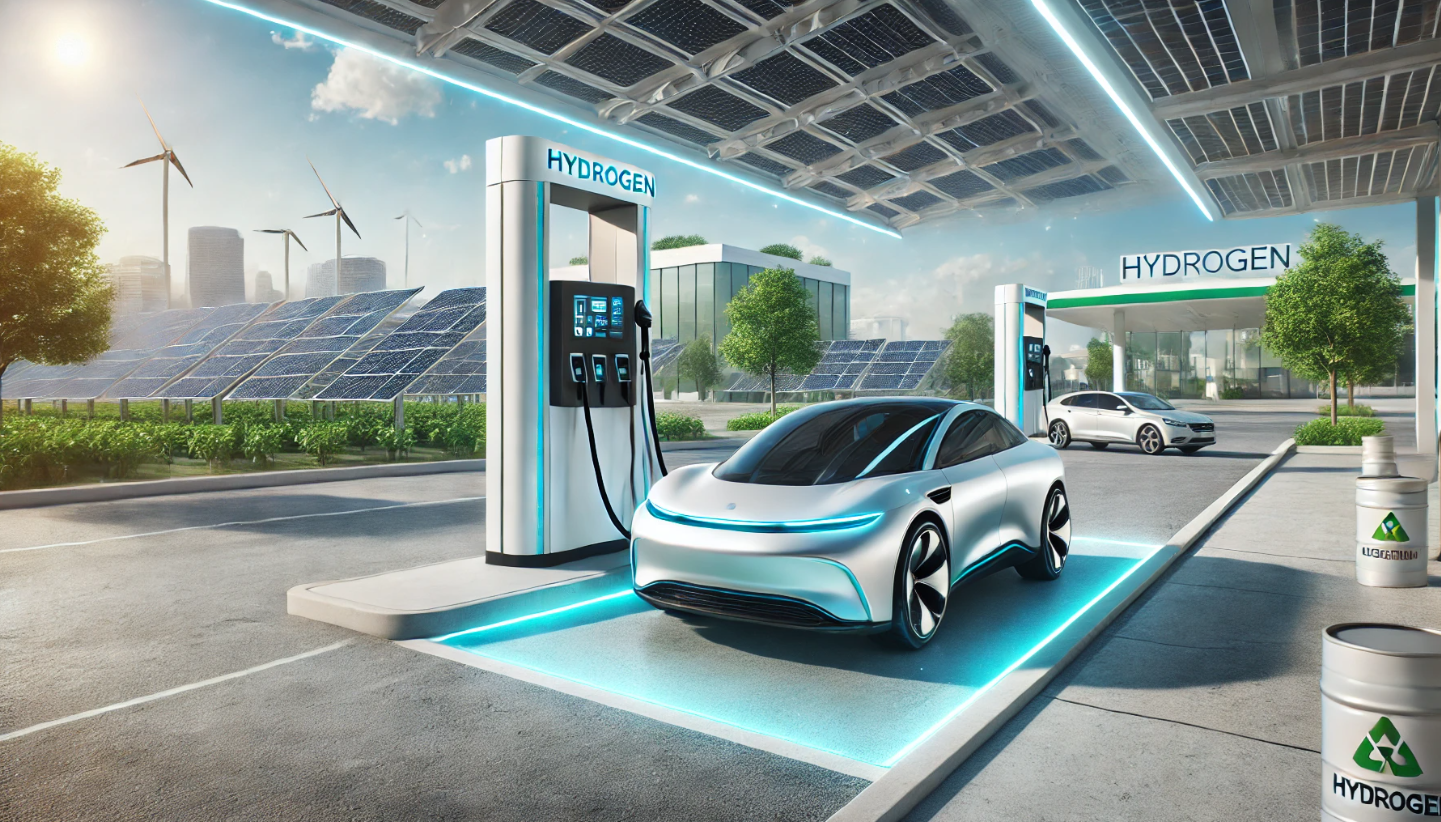
As the global automotive industry accelerates towards sustainable solutions, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) have emerged as a promising alternative to traditional internal combustion engines and battery electric vehicles (BEVs). With advancements in technology and infrastructure, FCVs are gaining attention for their potential to revolutionize the transportation sector. This article delves into the current state of hydrogen fuel cell technology, its advantages, challenges, and the future outlook of FCVs in the automotive landscape.
Understanding Hydrogen Fuel Cell Technology
Hydrogen fuel cells generate electricity through an electrochemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, producing only water and heat as byproducts. Unlike conventional engines that burn fuel, fuel cells convert chemical energy directly into electrical energy, offering a clean and efficient power source for vehicles.
How Fuel Cells Work
- Hydrogen Storage: Hydrogen gas is stored in high-pressure tanks within the vehicle.
- Electrochemical Reaction: Hydrogen is fed into the fuel cell stack, where it encounters a catalyst that splits it into protons and electrons.
- Electricity Generation: The electrons flow through an external circuit, creating electricity that powers the vehicle’s electric motor.
- Water Emission: Protons combine with oxygen from the air and the returning electrons to form water, which is emitted as the only exhaust.
Advantages of Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles
Environmental Benefits
- Zero Emissions: FCVs emit only water vapor, contributing to improved air quality and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
- Sustainable Fuel Source: Hydrogen can be produced from various renewable resources, including water electrolysis using solar or wind energy.
Performance and Convenience
- Quick Refueling: Hydrogen refueling takes approximately 3-5 minutes, comparable to conventional gasoline vehicles and significantly faster than recharging BEVs.
- Long Driving Range: FCVs offer ranges similar to traditional vehicles, often exceeding 300 miles on a single tank.
Energy Efficiency
- High Efficiency: Fuel cells are more efficient than internal combustion engines, converting a higher percentage of fuel energy into usable power.
Challenges Facing Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles
Infrastructure Development
- Limited Refueling Stations: The scarcity of hydrogen refueling infrastructure poses a significant barrier to widespread FCV adoption. Expanding this network requires substantial investment and coordination.
Production and Storage of Hydrogen
- Energy-Intensive Production: Most hydrogen is currently produced from natural gas through steam methane reforming, a process that emits carbon dioxide. Developing greener production methods, such as electrolysis powered by renewable energy, is essential.
- Storage and Transportation: Hydrogen’s low energy density necessitates high-pressure storage and poses challenges for transportation and distribution.
Cost Considerations
- High Vehicle Costs: The production of fuel cell systems and hydrogen storage tanks remains expensive, leading to higher vehicle prices compared to conventional and battery electric vehicles.
- Fuel Costs: Hydrogen fuel prices are relatively high due to production and distribution expenses.
Current Market and Industry Developments
Automaker Initiatives
Several major automakers are investing in hydrogen fuel cell technology:
- Toyota: The Mirai sedan, one of the first mass-produced FCVs, showcases Toyota’s commitment to hydrogen technology.
- Honda: The Clarity Fuel Cell offers a competitive range and quick refueling, emphasizing Honda’s focus on alternative energy vehicles.
- Hyundai: The NEXO SUV represents Hyundai’s advancements in fuel cell technology, featuring an impressive range and modern design.
Government Policies and Incentives
Governments worldwide are recognizing the potential of hydrogen in achieving climate goals:
- Subsidies and Grants: Financial incentives for FCV purchasers and hydrogen infrastructure development are being implemented in various regions.
- Regulatory Support: Policies promoting zero-emission vehicles and investments in research and development are fostering a conducive environment for FCV growth.
Future Outlook
The trajectory of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles depends on overcoming current challenges and leveraging opportunities:
- Technological Advancements: Ongoing research aims to reduce costs and improve the efficiency and durability of fuel cell systems.
- Infrastructure Expansion: Collaborative efforts between governments and private sectors are crucial to develop a comprehensive hydrogen refueling network.
- Market Adoption: As technology matures and infrastructure improves, consumer acceptance of FCVs is expected to increase, contributing to a more sustainable transportation ecosystem.
Conclusion
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles present a compelling solution in the quest for sustainable transportation, offering notable environmental benefits, convenience, and performance. While challenges remain, continued innovation, supportive policies, and infrastructure development are paving the way for hydrogen to become a significant player in the automotive industry’s green transition. As the world moves towards cleaner energy solutions, FCVs stand poised to complement battery electric vehicles and redefine the future of mobility.