The automotive industry has always been at the forefront of adopting new technologies to enhance safety, comfort, and personalization. From the introduction of seat belts and airbags to advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), each innovation has pushed the boundaries of how we interact with vehicles. In recent years, biometric interfaces have emerged as a groundbreaking advancement in the relationship between drivers and their cars. By integrating technologies such as fingerprint scanners, facial recognition, and iris scanning, automakers are creating vehicles that not only respond to voice and touch but also to the unique biological features of their users.
This evolution of biometrics in vehicles represents a shift toward a future where cars recognize their drivers as individuals rather than anonymous operators. Such personalization enhances security while simultaneously tailoring the driving experience to the needs and preferences of each user.
Fingerprint Recognition: The First Step Toward Biometric Driving
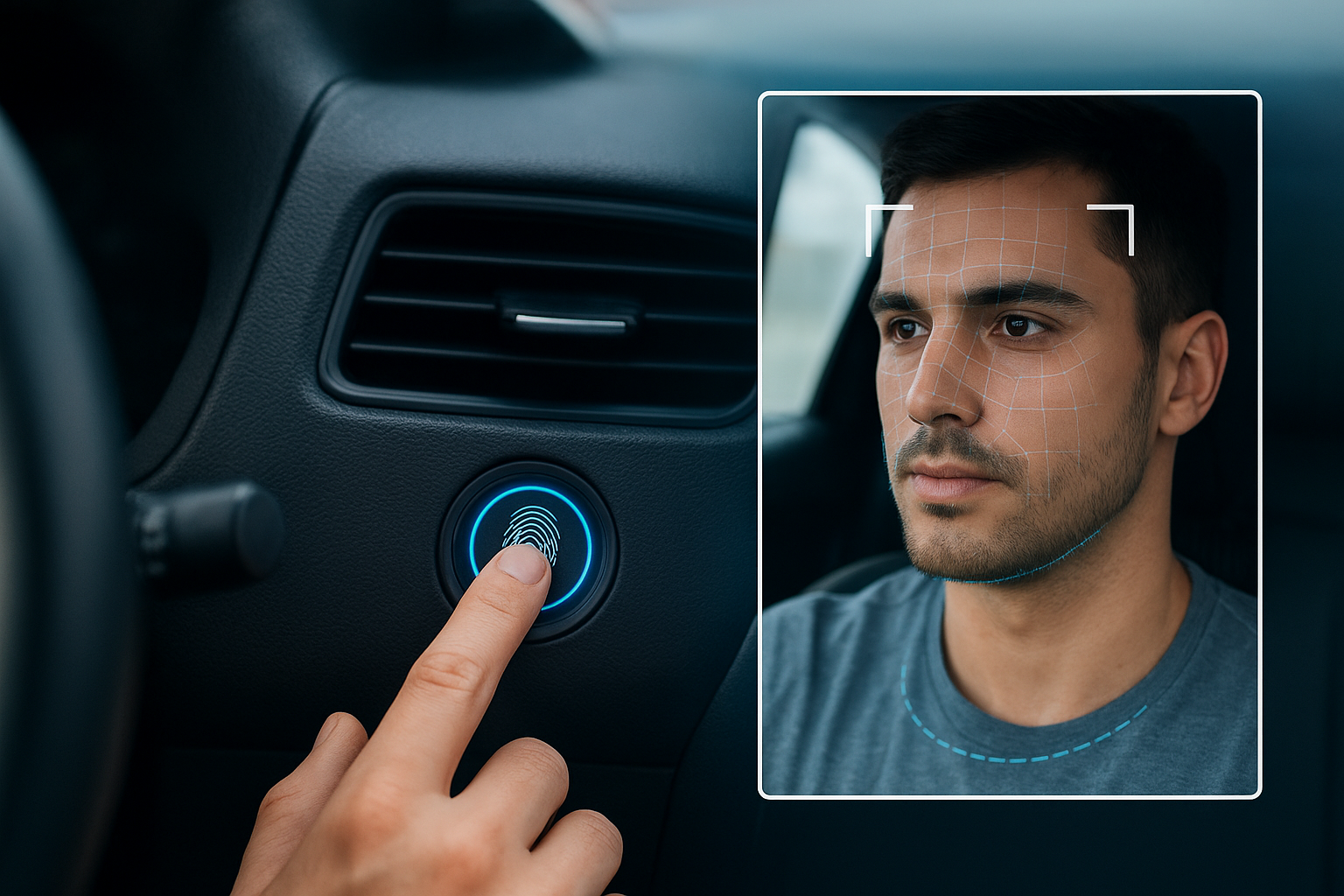
Fingerprint scanners are one of the earliest biometric technologies to be integrated into vehicles. Initially used in smartphones and laptops, fingerprint recognition quickly found its way into cars as a secure alternative to traditional keys. By scanning the driver’s fingerprint, the vehicle can unlock doors, start the engine, and even restrict unauthorized access.
Beyond security, fingerprint recognition opens the door to highly personalized settings. A simple touch of the sensor can adjust seat positions, climate control, and infotainment preferences according to the registered driver’s profile. This eliminates the need for manual adjustments and ensures comfort every time the car is used.
Facial Recognition: Adding a Layer of Intelligence
Facial recognition takes biometrics to the next level by combining security with intelligent monitoring. Using cameras and advanced algorithms, vehicles can identify the driver before unlocking and starting. This technology prevents unauthorized access and adds convenience by recognizing family members or frequent users without requiring physical contact.
More importantly, facial recognition contributes to safety beyond entry. Modern systems can track the driver’s eyes and facial expressions to detect signs of drowsiness or distraction. By alerting the driver or even activating emergency systems, facial recognition helps prevent accidents caused by fatigue—a growing concern in long-distance travel and daily commutes.
Iris Scanning: The Future of Ultra-Secure Vehicles
While still in its early stages, iris recognition is seen as one of the most secure biometric technologies. Each person’s iris pattern is unique and nearly impossible to replicate, making it an ideal tool for high-security vehicles or luxury models. In cars, iris scanning could be used not only for unlocking and starting the engine but also for authorizing digital payments, accessing sensitive data, or enabling parental controls.
Although iris recognition currently faces challenges such as cost and complexity, it represents the cutting edge of biometric integration. As sensors become more affordable and compact, it is expected that iris scanning will play a greater role in the automotive market.
Enhancing Security Through Biometrics
One of the main drivers behind the adoption of biometrics in cars is the need for improved security. Traditional car keys and even smart key fobs are vulnerable to theft or cloning. By contrast, biometric data cannot be easily duplicated, offering a stronger defense against car theft.
Additionally, biometrics provide multi-layered authentication. A car could require both fingerprint and facial recognition before starting, making unauthorized access nearly impossible. This is particularly valuable for car-sharing services, luxury brands, and regions with high crime rates.
Personalization: Making Cars Truly Individual
Biometrics are not just about security—they also transform how cars adapt to their drivers. When a vehicle recognizes its user through fingerprint, face, or iris scanning, it can instantly recall a tailored environment. Seat height, mirror angles, steering wheel position, radio stations, and even navigation routes can be personalized without manual input.
For families who share a vehicle, this feature is especially valuable. Each member can enjoy a unique driving experience without having to reconfigure the car every time they switch seats. In luxury vehicles, this personalization becomes part of the brand’s promise to deliver comfort and exclusivity.
Challenges and Concerns
Despite the potential benefits, biometric technology in cars also raises challenges. Privacy concerns are among the most significant. Storing sensitive biometric data requires robust cybersecurity measures to prevent misuse. Manufacturers must ensure that data is encrypted, stored securely, and never shared without user consent.
Another concern is reliability. Factors such as dirt, lighting conditions, or injuries to fingers or face could interfere with biometric recognition. For this reason, biometric systems are often combined with backup methods such as PIN codes or smart keys.
The Road Ahead: Integration with Autonomous Driving
As the automotive industry moves toward autonomous vehicles, biometrics will play an even greater role. In a self-driving car, where passengers may have minimal physical interaction with the controls, biometrics can ensure that the right person is using the vehicle. Combined with AI, biometric systems could also monitor passengers’ health, detect stress levels, and adjust the driving style or cabin environment accordingly.
This integration will not only make cars more secure but also transform them into intelligent companions that respond to human emotions and well-being.
Conclusion
The evolution of biometric interfaces in cars marks a significant step forward in the way we experience driving. From the convenience of fingerprint recognition to the intelligence of facial monitoring and the ultra-security of iris scanning, biometrics are reshaping vehicles into safer, smarter, and more personalized machines.
As automakers continue to embrace these technologies, the future promises a driving experience where cars know their users as well as—or even better than—the drivers know themselves. In this future, safety and personalization are no longer separate goals but two sides of the same technological revolution.