Over the last decade, the automotive industry has undergone a technological revolution. While safety features such as blind-spot sensors and adaptive cruise control have received much attention, another equally transformative development is happening inside the cabin: the rise of in-car voice assistants powered by artificial intelligence. These systems, once limited to simple navigation commands or music playback, are now evolving into complex digital companions that enhance driving safety, efficiency, and convenience.
From Basic Commands to Intelligent Interactions
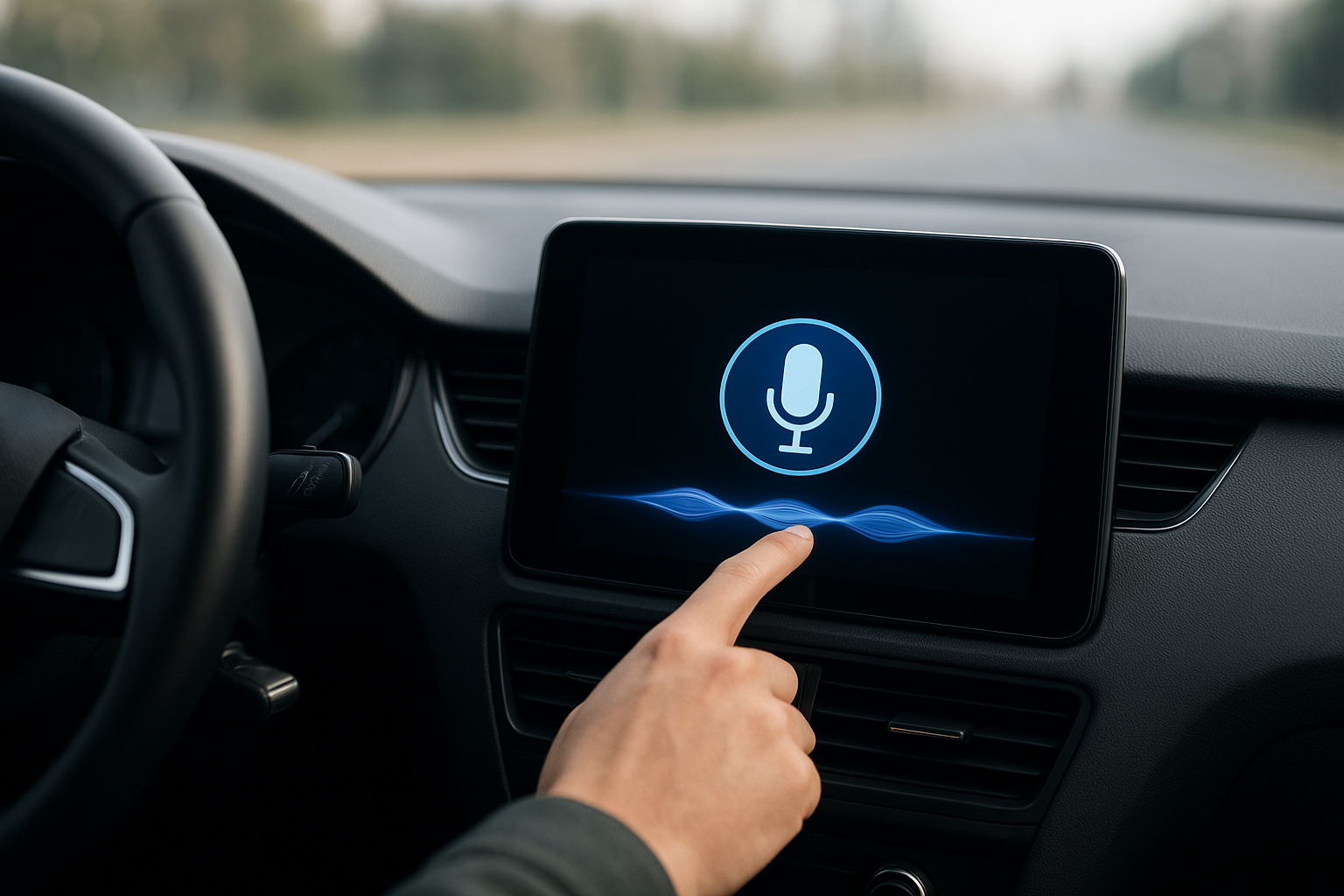
Early in-car voice systems often frustrated drivers with poor accuracy and limited functionality. Commands had to be spoken in a rigid format, and background noise frequently interfered with recognition. However, advancements in natural language processing and AI-driven speech recognition have dramatically changed the experience.
Modern voice assistants can understand conversational language, interpret context, and even anticipate driver needs. For example, instead of saying “Navigate to 125 Main Street,” a driver can now say, “Find me the nearest coffee shop on the way to work,” and the system will deliver results tailored to both preference and location.
Safety Benefits of Hands-Free Interaction
One of the strongest arguments for in-car voice assistants is their role in reducing driver distraction. Smartphones remain one of the leading causes of road accidents, as drivers attempt to type messages or scroll through apps while on the move. By shifting these tasks to a voice-activated interface, drivers can keep their hands on the wheel and eyes on the road.
Voice assistants can send and read messages, adjust climate settings, or change music without requiring physical interaction. This hands-free approach directly supports road safety initiatives, aligning with regulations in many countries that discourage manual phone use while driving.
Personalized Driving Experiences
Artificial intelligence allows voice assistants to learn from driver behavior. Over time, the system can recognize preferred routes, favorite playlists, or frequently visited destinations. This personalization extends beyond convenience—it creates a sense of familiarity and comfort, making the driving experience smoother and more enjoyable.
Some systems are even integrated with smart home devices, enabling drivers to adjust home thermostats, turn on lights, or check security cameras before arriving. The car becomes an extension of the driver’s digital ecosystem, blending mobility with everyday living.
Integration with Advanced Vehicle Systems
Voice assistants are no longer limited to controlling media or navigation. In next-generation vehicles, they are increasingly integrated with core systems such as performance monitoring, diagnostics, and safety alerts. A driver might ask about tire pressure, fuel efficiency, or even upcoming maintenance needs, and the assistant can provide real-time feedback.
This level of integration transforms the assistant into more than just a convenience—it becomes a proactive tool for vehicle care and driver awareness. For electric vehicles, assistants can manage charging schedules, suggest nearby charging stations, and optimize battery usage based on trip length.
Challenges and Privacy Concerns
Despite their benefits, in-car voice assistants raise important questions about privacy and data security. Many systems rely on cloud processing, meaning driver interactions are transmitted to external servers. This data could potentially reveal personal habits, locations, and preferences. Manufacturers must therefore balance innovation with robust security protocols and transparent data policies.
Another challenge lies in ensuring inclusivity. Voice recognition systems must adapt to different accents, languages, and speech patterns. Failure to do so risks excluding users or creating frustration that undermines the technology’s potential.
The Road Ahead
The future of in-car voice assistants is closely tied to the development of autonomous vehicles. In a driverless car, where the human role shifts from controlling the vehicle to managing the journey, voice interfaces will become the primary way passengers interact with the system.
We can expect assistants to evolve into multi-modal companions, combining voice with gesture recognition, eye-tracking, and haptic feedback. They may even adopt emotional intelligence, adjusting tone and responses based on driver mood or stress levels.
Conclusion
In-car voice assistants are no longer futuristic novelties—they are becoming central to the driving experience. By improving safety, enhancing personalization, and integrating with broader digital ecosystems, they redefine what it means to interact with a vehicle.
While challenges in privacy and inclusivity remain, the trajectory is clear: AI-powered voice assistants are shaping the future of mobility, making driving smarter, safer, and more connected than ever before. For drivers and passengers alike, the car of tomorrow will not just be a machine—it will be a conversation partner.