The year 2024 has been transformative for the global automotive industry, marked by technological advancements, regulatory shifts, and changing consumer preferences. From the rise of electric vehicles to significant geopolitical impacts on production and trade, here’s a comprehensive overview of the key developments that defined the automotive world in 2024.
Electric Vehicles (EVs) Take Center Stage
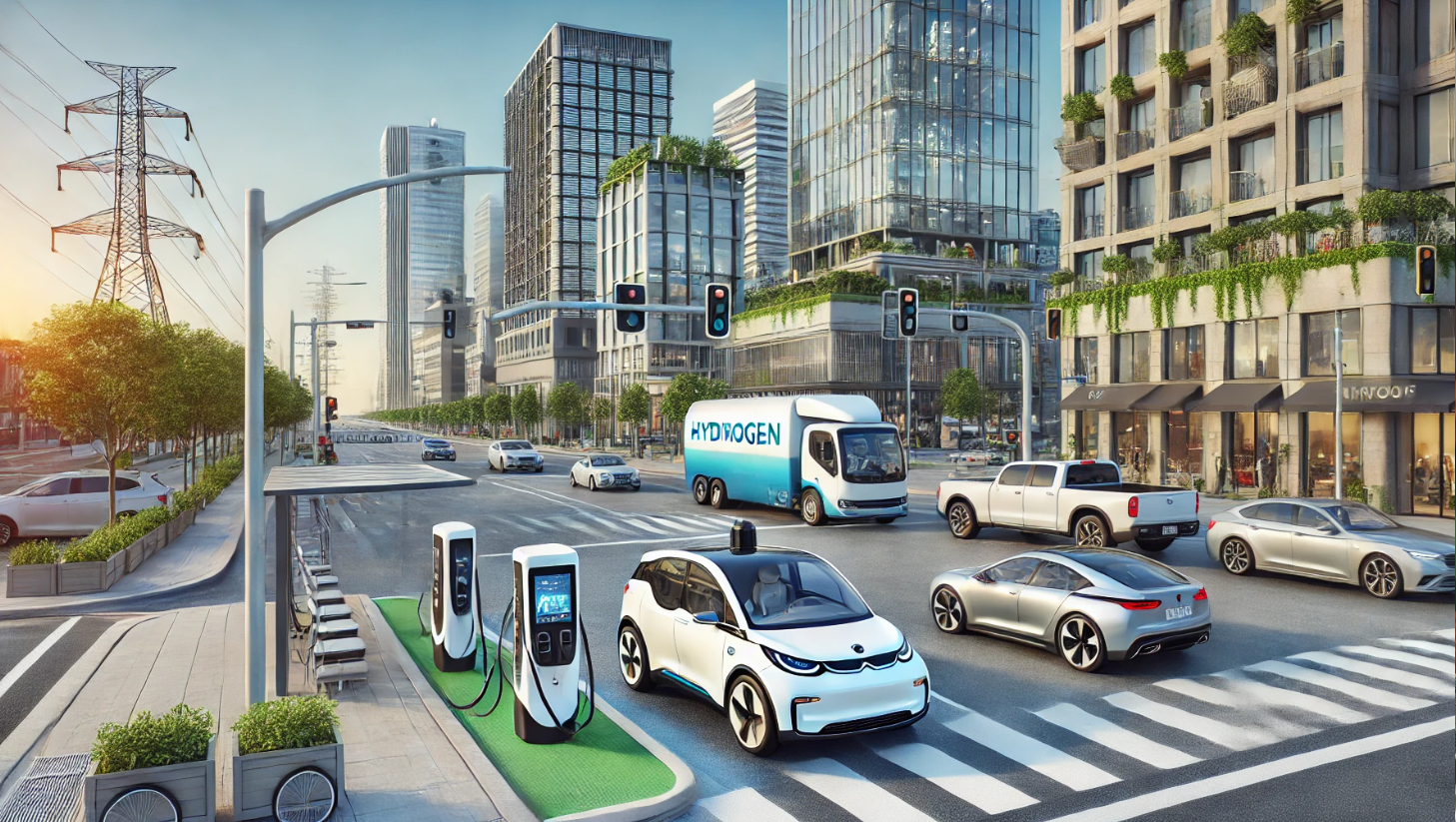
One of the most notable trends of 2024 has been the accelerated adoption of electric vehicles (EVs). Governments worldwide intensified their push towards sustainability, implementing stricter emissions regulations and providing incentives for EV adoption.
In the United States, the Inflation Reduction Act continued to fuel the EV market, with major manufacturers like Tesla, Rivian, and Ford increasing production of electric trucks and SUVs. Tesla unveiled its highly anticipated Cybertruck, finally entering mass production and reshaping the electric utility vehicle segment.
In Europe, Volkswagen released its all-electric ID.7 sedan, targeting premium markets and competing directly with Tesla’s Model S. Meanwhile, startups like Polestar expanded their reach with innovative designs and sustainable production processes.
China, the world’s largest EV market, witnessed record sales of electric cars, with BYD and NIO leading the charge. BYD’s Seal EV gained significant popularity, providing stiff competition to Tesla’s Model 3 in the region.
Breakthroughs in Autonomous Driving
2024 also saw remarkable advancements in autonomous driving technology. Alphabet’s Waymo and GM’s Cruise expanded their robo-taxi services to more cities across the United States. In Europe, Mercedes-Benz became the first automaker to receive Level 3 autonomy certification for use on German highways.
China made headlines by deploying its first large-scale autonomous bus fleet in major cities like Shanghai and Shenzhen. The buses, equipped with advanced AI systems, demonstrated the feasibility of autonomous public transportation in urban areas.
Despite these advancements, regulatory hurdles and public skepticism remain significant barriers to widespread adoption. High-profile accidents involving autonomous vehicles continued to spark debates about safety and liability.
Global Supply Chain Challenges Persist
The lingering effects of the COVID-19 pandemic and ongoing geopolitical tensions, particularly the conflict between Russia and Ukraine, continued to disrupt global supply chains in 2024. Semiconductor shortages, though less severe than in previous years, still posed challenges for automakers.
Europe’s automotive sector faced additional difficulties as energy prices soared due to reduced natural gas supplies. Automakers such as Stellantis and Renault announced temporary factory closures, citing high production costs.
In contrast, the United States experienced a rebound in production, thanks to domestic semiconductor manufacturing initiatives. President Biden’s CHIPS Act provided substantial funding for U.S.-based chipmakers, helping reduce reliance on imports from Asia.
Sustainability and Circular Economy Initiatives
Sustainability remained a focal point for the automotive industry. Leading manufacturers adopted circular economy principles, emphasizing recycling and reuse. BMW introduced its “Neue Klasse” concept, showcasing vehicles made from 70% recycled materials.
Volvo committed to becoming a fully electric car brand by 2030, with plans to achieve carbon neutrality across its supply chain by 2040. Similarly, Toyota announced breakthroughs in solid-state battery technology, promising higher energy density and shorter charging times for its future EVs.
Rising Popularity of Hydrogen-Powered Vehicles
Hydrogen emerged as a viable alternative to battery-electric vehicles, particularly for heavy-duty applications. Hyundai and Toyota expanded their hydrogen fuel cell offerings, launching new trucks and buses capable of long-range operation.
In Japan, the government increased investment in hydrogen infrastructure, aiming to position the country as a leader in the hydrogen economy. Europe followed suit, with Germany and the Netherlands building extensive networks of hydrogen refueling stations.
Geopolitical Developments Impacting the Industry
Geopolitical events significantly influenced the automotive landscape in 2024. Sanctions on Russia led to a further decline in its automotive exports, while Chinese automakers capitalized on the void, increasing exports to Africa, the Middle East, and South America.
Trade tensions between the U.S. and China intensified, affecting the flow of critical materials like lithium and rare earth metals. In response, automakers diversified their supply chains, with many sourcing materials from Australia and South America.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Consumer preferences continued to evolve in 2024. Compact SUVs remained the most popular vehicle segment globally, reflecting a balance between utility and efficiency. In emerging markets, affordable small cars gained traction as inflation pressured household budgets.
Luxury carmakers such as Rolls-Royce and Bentley reported record sales, driven by rising demand in Asia and the Middle East. Meanwhile, subscription-based car ownership models gained popularity, particularly in urban areas, offering flexibility without the burden of traditional ownership.
Outlook for 2025 and Beyond
The trends observed in 2024 suggest a dynamic future for the automotive industry. Electric and autonomous vehicles will continue to shape the market, while geopolitical and economic factors will influence production and trade. Automakers that adapt to these changes and prioritize sustainability are likely to thrive in the years ahead.
As the industry accelerates towards innovation and sustainability, 2024 will be remembered as a pivotal year that set the stage for a cleaner, smarter, and more connected future in mobility.