In recent years, urban landscapes have witnessed a significant transformation in personal transportation modes. Amid growing concerns about environmental sustainability, traffic congestion, and the quest for healthier lifestyles, bicycles and their electric counterparts, e-bikes, have emerged as pivotal solutions. This article delves into the evolution of these personal urban transport options, their technological advancements, and their broader implications for city living.
The Resurgence of Bicycles in Urban Settings
Bicycles, once considered a relic of the past in many urban areas dominated by motor vehicles, have experienced a renaissance. This resurgence can be attributed to several factors:
- Environmental Awareness: As cities grapple with air pollution and carbon emissions, bicycles offer a zero-emission mode of transport, aligning with global sustainability goals.
- Health Benefits: Cycling promotes cardiovascular health, aids in weight management, and enhances mental well-being, making it an attractive option for health-conscious urbanites.
- Economic Efficiency: With rising fuel costs and urban living expenses, bicycles present a cost-effective alternative to motorized transport.
Technological Innovations in Traditional Bicycles
The modern bicycle has undergone numerous technological enhancements to cater to the urban commuter:
- Lightweight Materials: The adoption of materials like carbon fiber and aluminum has resulted in lighter yet durable frames, enhancing maneuverability and speed.
- Advanced Gear Systems: Modern gearing mechanisms provide smoother transitions and adaptability to varied terrains, making urban commuting more efficient.
- Enhanced Safety Features: Innovations such as integrated lighting systems, reflective coatings, and improved braking mechanisms have bolstered cyclist safety in bustling city environments.
The Advent and Integration of E-Bikes
E-bikes, or electric bicycles, have revolutionized personal urban transportation by combining the traditional cycling experience with electric propulsion. Their rise in popularity stems from:
- Assisted Pedaling: E-bikes are equipped with electric motors that assist riders, especially during acceleration or uphill climbs, reducing physical exertion and making cycling accessible to a broader demographic.
- Extended Range: With battery advancements, e-bikes allow commuters to travel longer distances without fatigue, bridging gaps that might be challenging with conventional bicycles.
- Technological Features: Many e-bikes come integrated with smart technologies, including GPS navigation, fitness tracking, and connectivity with mobile applications, enhancing the overall user experience.
Impact on Urban Infrastructure and Mobility
The proliferation of bicycles and e-bikes has prompted cities to rethink and redesign their infrastructures:
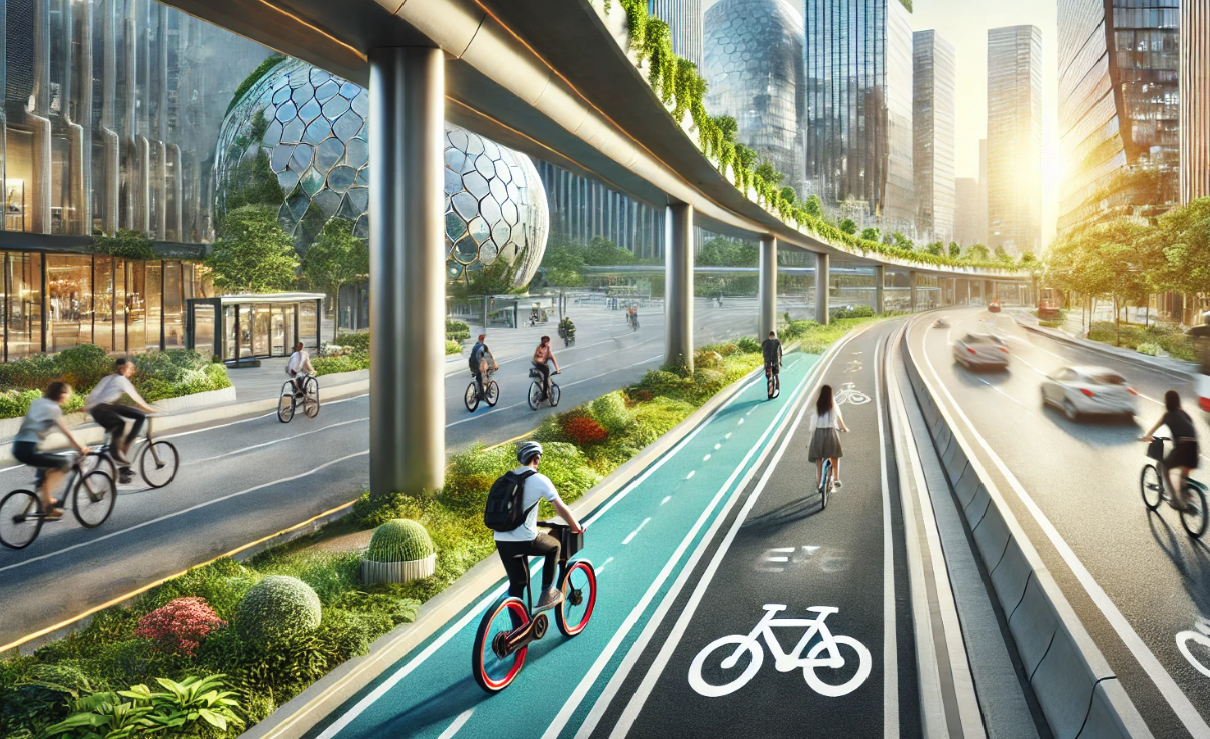
- Dedicated Bike Lanes: To ensure safety and encourage cycling, many urban areas have introduced dedicated bike lanes, segregating cyclists from motor vehicle traffic.
- Bike-Sharing Programs: Cities worldwide have launched bike-sharing initiatives, providing residents and tourists with affordable and convenient access to bicycles. For instance, Moscow’s «Велобайк» system, initiated in 2013, expanded from 79 stations with 550 bicycles to over 629 stations with 6,500 bicycles by 2020, including 400 e-bikes. In the 2019 season alone, users completed over 5 million trips, highlighting the system’s success and popularity.
- Parking and Charging Stations: The rise of e-bikes necessitates the development of charging infrastructure. Urban planners are now incorporating charging stations and secure parking facilities to accommodate this growing mode of transport.
Challenges and Considerations
While the shift towards bicycles and e-bikes offers numerous benefits, several challenges need addressing:
- Regulatory Frameworks: The classification of e-bikes varies across regions, leading to inconsistencies in traffic laws, speed limits, and safety standards. Establishing clear regulations is crucial for harmonious road sharing.
- Safety Concerns: The integration of e-bikes, which can achieve higher speeds than traditional bicycles, raises safety issues, especially in mixed-traffic scenarios. Enhancing public awareness and implementing safety campaigns are essential.
- Infrastructure Adaptation: Rapid adoption of these personal transport modes can strain existing infrastructures. Cities must proactively invest in expanding and maintaining cycling paths and related amenities.
The Future of Personal Urban Transportation
The trajectory of personal urban transportation points towards a more integrated and multimodal approach:
- Technological Synergy: The convergence of technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence, can lead to smarter e-bikes capable of real-time data analysis, route optimization, and predictive maintenance.
- Sustainable Urban Planning: Embracing bicycles and e-bikes aligns with the broader vision of sustainable cities, reducing reliance on fossil fuels, lowering greenhouse gas emissions, and promoting green spaces.
- Cultural Shift: As cycling becomes more ingrained in urban culture, it fosters a sense of community, encourages outdoor activities, and promotes a healthier populace.
Conclusion
Bicycles and e-bikes have undeniably carved a niche in the urban transportation ecosystem. Their rise reflects a collective shift towards sustainable, efficient, and health-conscious mobility solutions. As technology continues to evolve and cities adapt, these personal transport modes are poised to play an even more significant role in shaping the future of urban commuting.